Plant Performance Testing
Our field service teams specialize in combustion optimization programs through the application of the fundamentals. Our programs have a very unique method of using specialized testing equipment to discover performance improvements for nearly any steam generator.
-
Heat Rate Improvement
-
Reliability Improvements
-
Establishment of Performance Based Maintenance
Storm Technologies technical field services team is comprised of specialists that are trained in the field of comprehensive diagnostic testing and outage services with a “results” oriented approach. Our field services team specializes in Combustion Optimization programs through the application of the fundamentals.
Our programs have a very unique method of combining specialized testing equipment and detailed outage services to determine improvements of nearly any steam generator.
These improvements include:
- Combustion and Boiler Efficiency
- Heat Rate Improvements
- Environmental Compliance
- Reliability Opportunities
Furthermore, we believe that our comprehensive approach of reviewing the performance of the entire system and inter-relating the variables of performance with fuel quality, reliability, and operations is our niche. Whatever the need is. We stand behind our motto which is…Service, Quality, and Results.
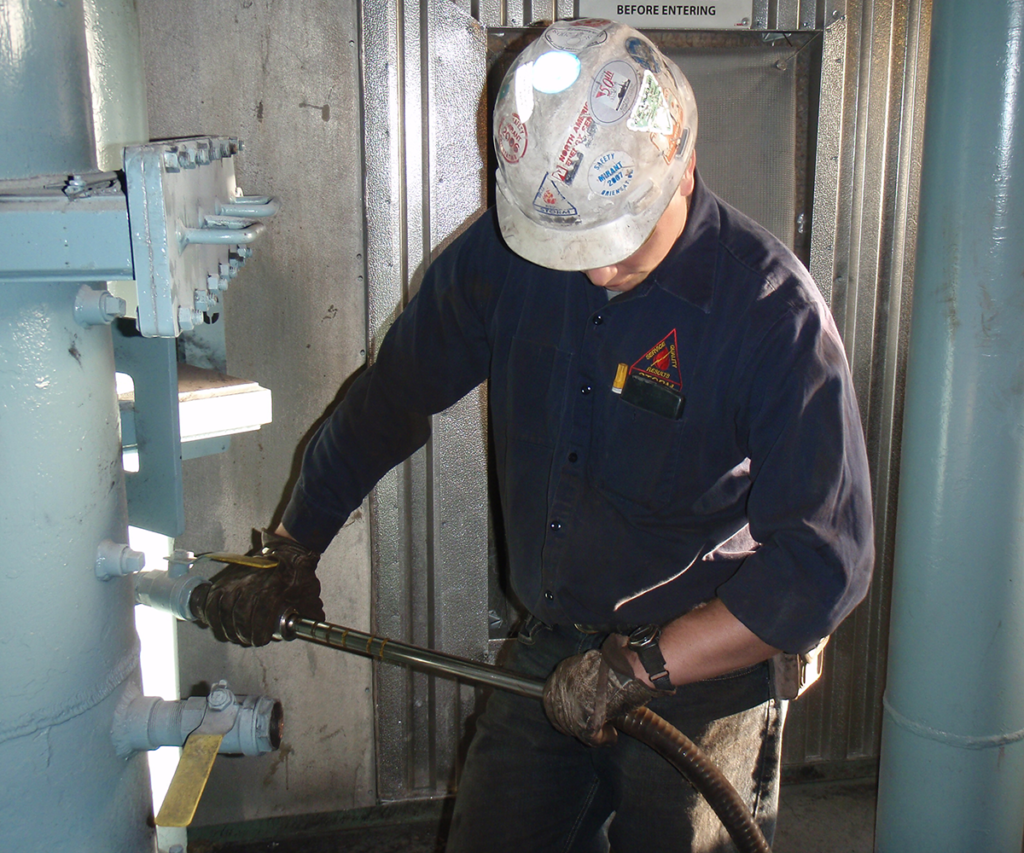
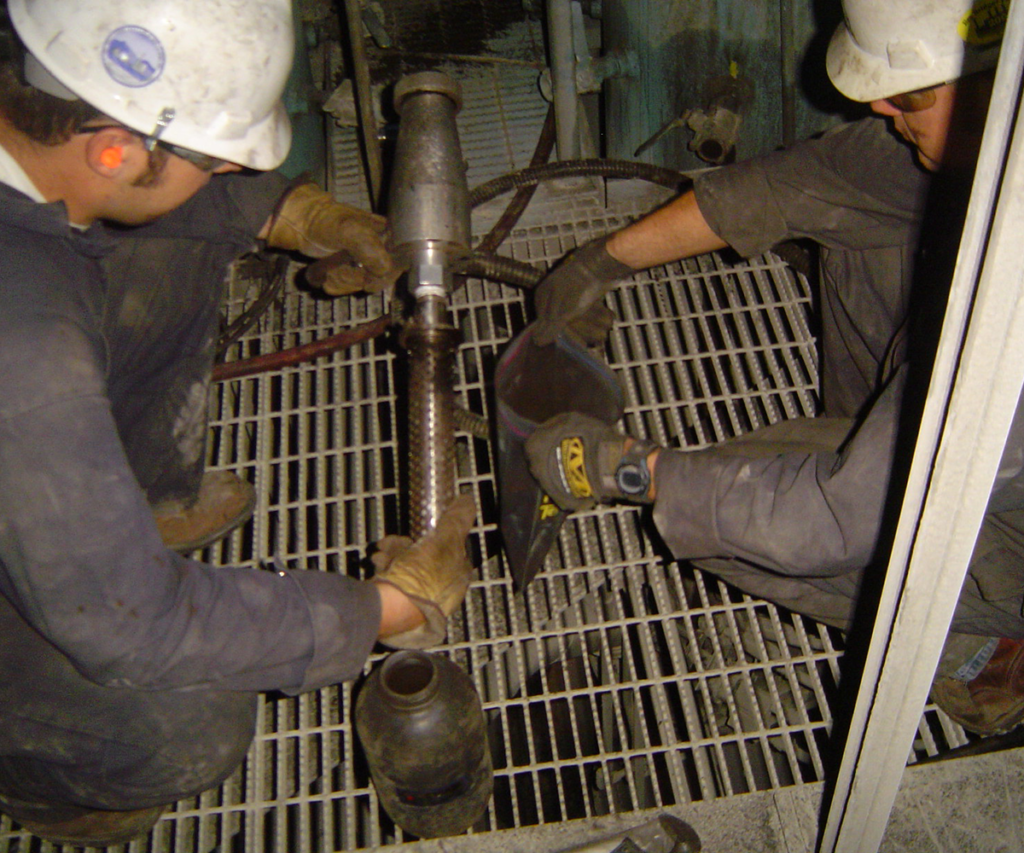
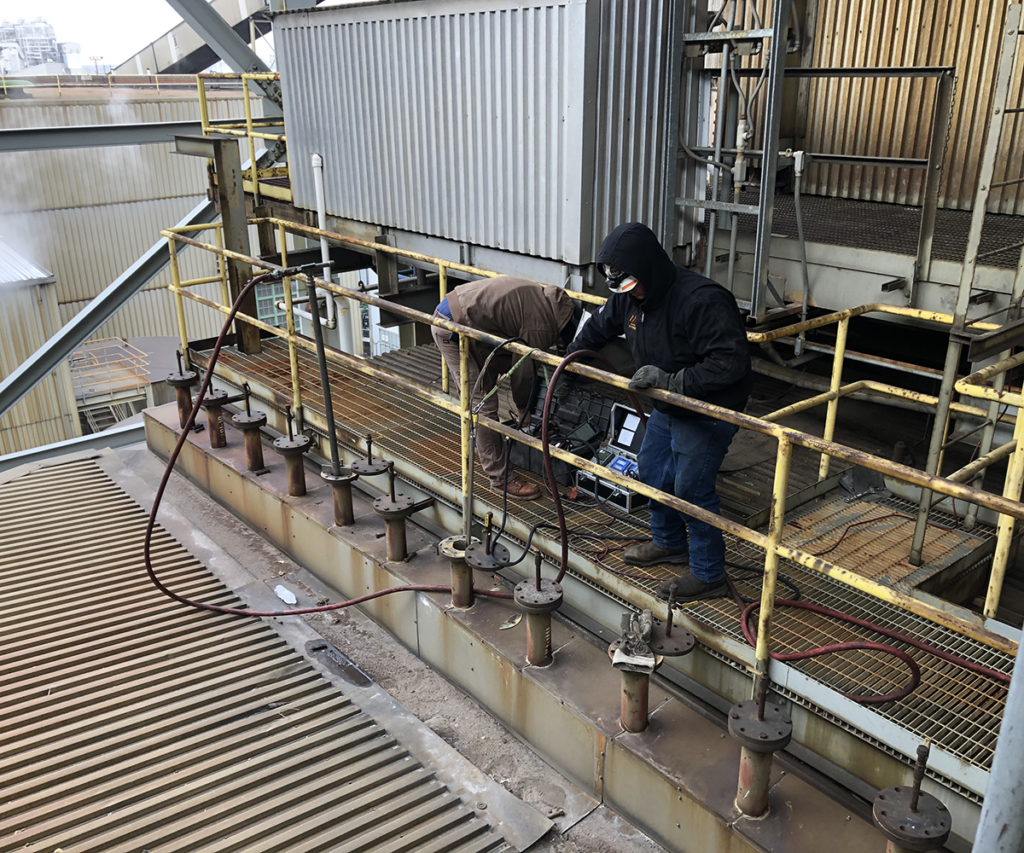
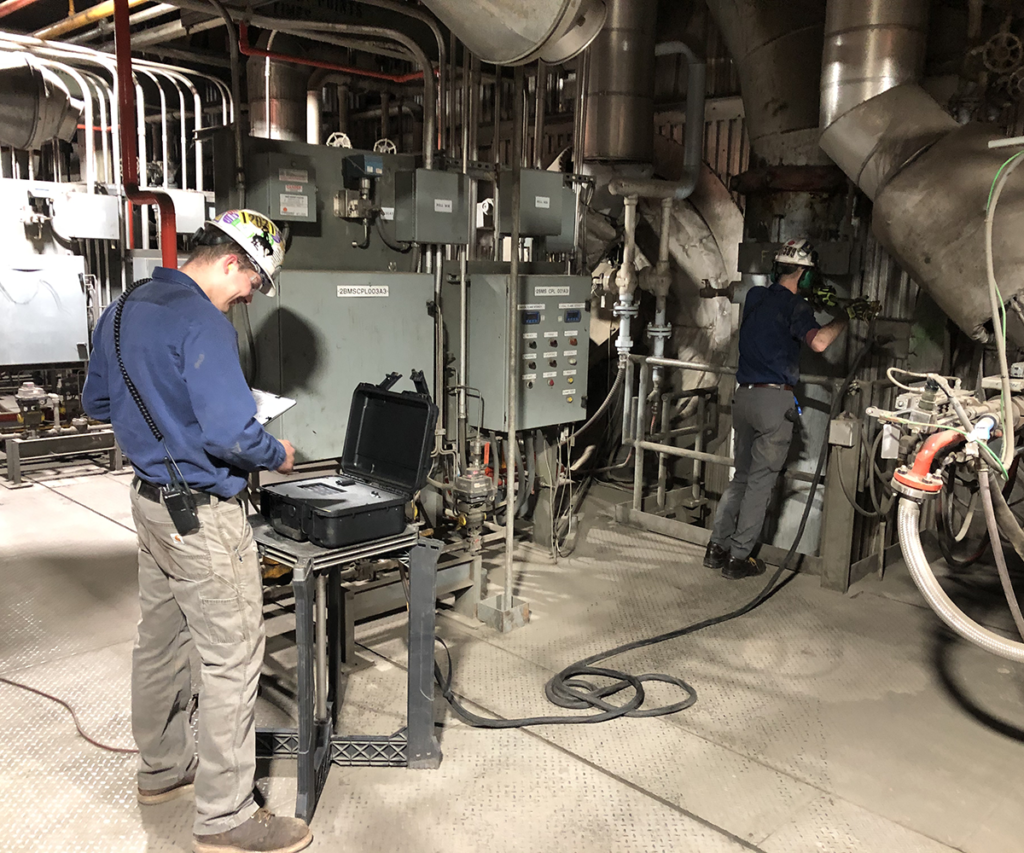
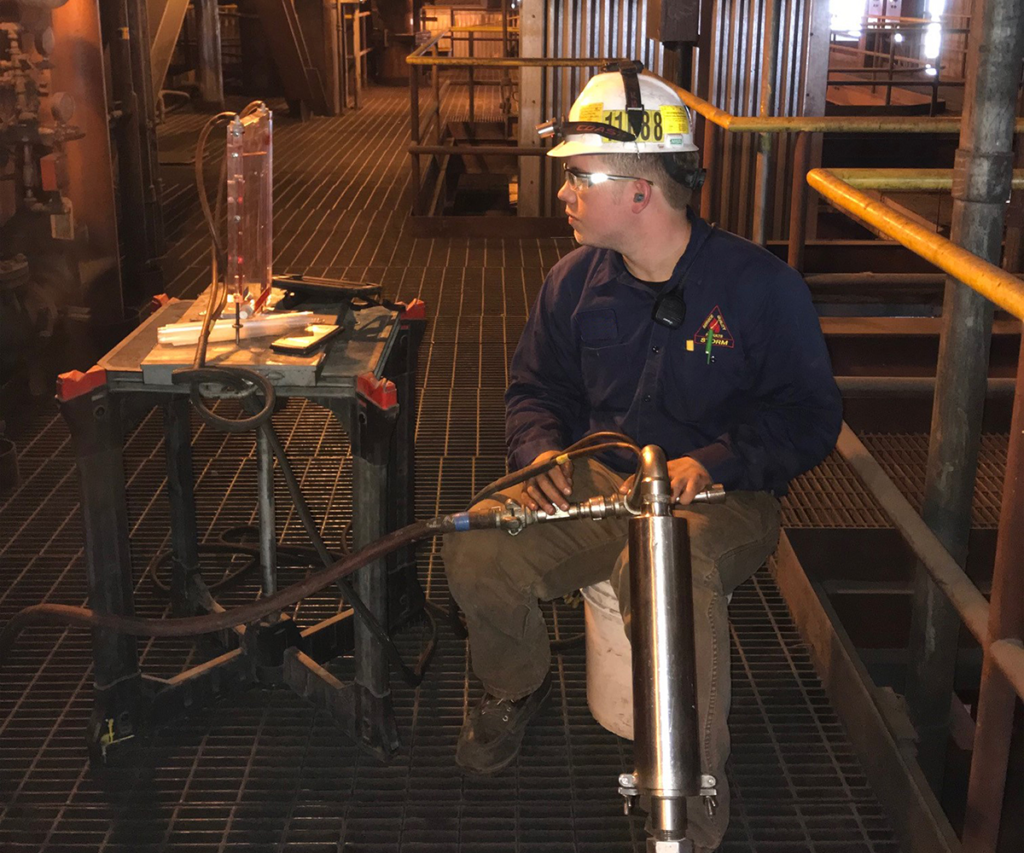
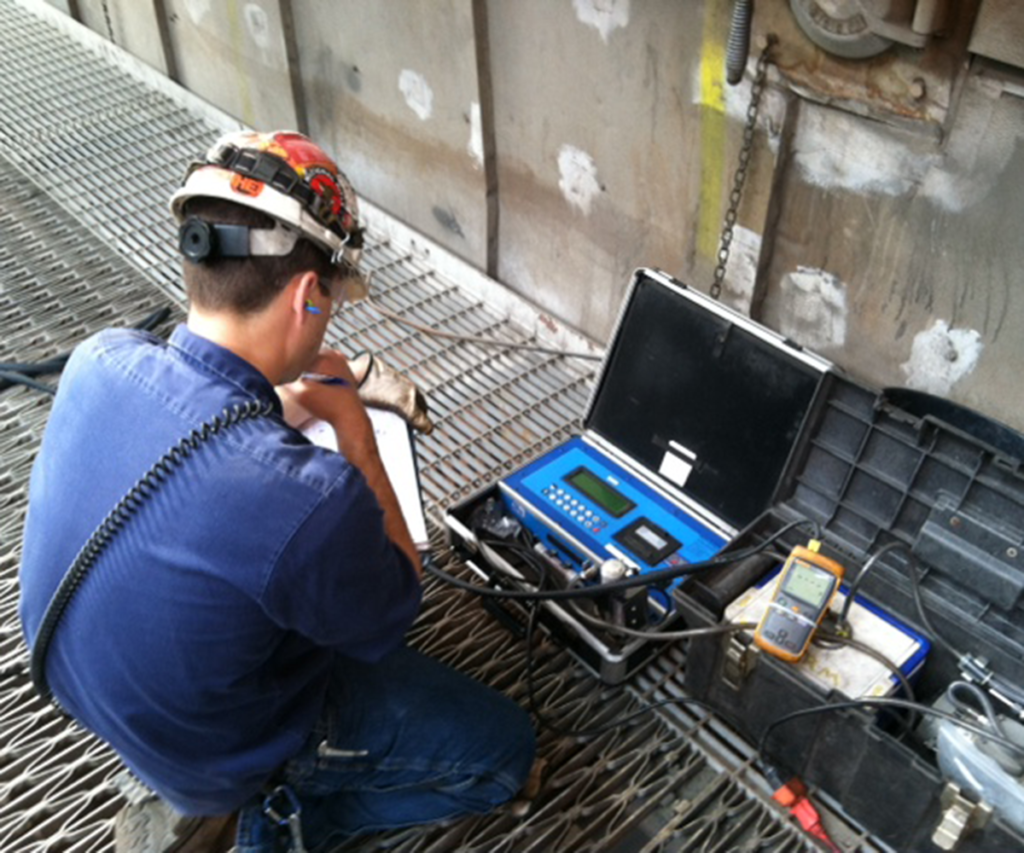
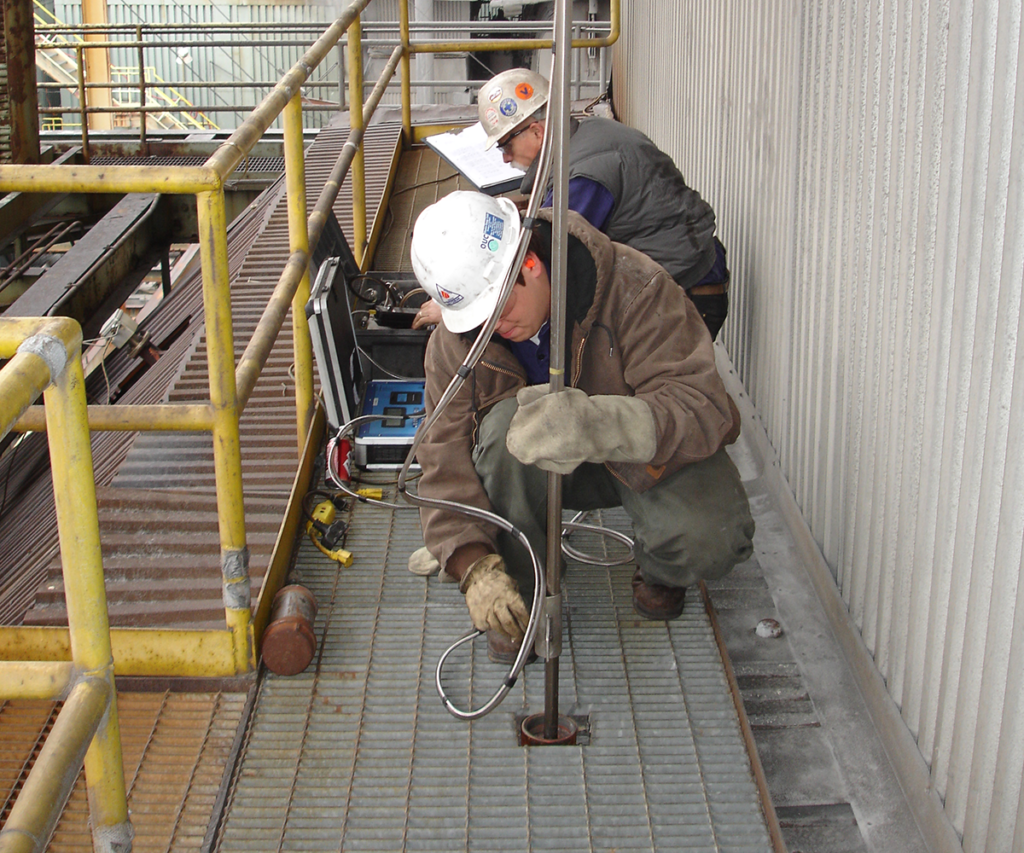







Typical locations for conducting a comprehensive test
In addition to testing services, Storm’s professional team has the experience and expertise to support your next scheduled or forced outage with performance inspections of the burners, pulverizers, fans, flue gas ductwork, penthouse and air heater. Storm can also provide in-depth management of air heater outage overhauls from planning to execution of the overhaul.
Reason for Inspections:
- Throughout the years Storm has found that coupling the professional testing services along with outage support through performance inspections that performance challenges associated with poor combustion, elevated heat rates and decreased reliability can be effectively improved. Storm’s personnel often complete inspections on overlooked items that are critical to combustion but are too tedious to be included in many outage plans, such as burner centering, stroking burner registers and damper inspections to name a few. Furthermore, Storm’s fabrication shop can provide last minute fabricated components that may be needed once identified during your outage.
- Storm also has the expertise to provide complete outage services for your upcoming overhaul on regenerative Ljungstrom air heaters. Storm can provide the outage planning, scheduling and provide you with quotes for replacement parts to ensure your air heater is performing well following the outage.
Boiler Performance Testing
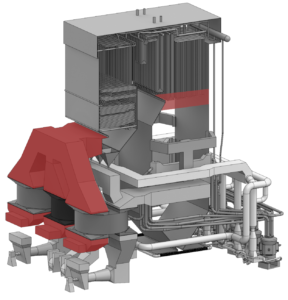
Storm evaluates boiler performance by measuring flue gas constituents of temperature, oxygen, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides throughout the boiler and back-pass. Measurements typically obtained by Storm include the following locations:
- Furnace Exit (At the nose arch or just above the nose arch)
- Economizer Exit/Air Heater Inlet
- Air Heater Outlet
Reason for Testing:
Measurements at these locations can uncover areas of concern such as, reducing atmospheres, high FEGT, slagging and decreased performance, in-leakage, etc. Storm still utilizes a water-cooled HVT probe when conducting a complete boiler performance test. This is a very important step, that other companies often overlook. By evaluating the in-furnace conditions of the boiler our teams can get a better idea of the root cause of combustion related issues. Obtaining and analyzing flyash LOI is also critical in determining overall performance. By utilizing these locations, an abbreviated boiler efficiency can be obtained along with APH performance and system leakage of the boiler and APH.
Testing Equipment:
Furnace Exit Testing
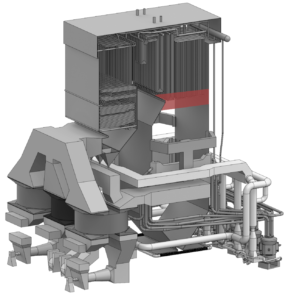
Testing to measure the temperature and gas constituents of at the furnace exit. Furnace exit testing is a vital part of improving overall combustion and optimizing unit performance.
Reason for Testing:
Furnace Exit Testing is important because it quantifies the concentration of Oxygen (O2 , %), Nitrous Oxides (NOX ppm) and Carbon Monoxide (CO , ppm) inside the furnace, typically at the nose arch elevation. One of the most important reasons for conducting this test is determining the actual excess oxygen levels within the furnace. Balanced draft boilers over time will develop leaks that will allow tramp air to infiltrate the boiler and flue gas duct work. If the tramp air is introduced into the system upstream of the excess oxygen probes then the boiler airflow control will account for this additional oxygen and reduce the total air to the boiler for combustion, often times leaving the furnace in a severely sub-stoichiometric firing condition with reducing atmospheres present. Furthermore, Furnace Exit Testing allows the plant to quantify the Furnace Exit Gas Temp (FEGT) as well as make a profile that depicts the specific environment of the furnace based on temperatures and gas constituents. This is important because it reveals all area’s of concerns inside the furnace. Common concerns found inside the boiler are reducing atmospheres, high FEGT, and low oxygen. These issues directly relate to an increase in slagging and decreased performance/efficiency.
Testing Equipment:
- High Velocity Thermocouple (HVT) Probe
- Gas Sampling Conditioner Kit
- Portable Gas Analyzer
STORM testing services also includes the ability and knowledge to complete environmental emissions testing for particulate matter (EPA Methods 5 and 17), NOX, CO and SO2.
Reason for Testing:
To better understand the efficiency of your air pollution control equipment. Particulate matter testing can be utilized to evaluate the flyash loading in your system or to determine the effectiveness of your ESP or baghouse. Further, flue gas testing can be done to evaluate the flue gas profiles and concentrations from the furnace exit to the ID fan in order to provide our customer with the flue gas measurements needed
AIG (SCR) Tuning

Ammonia Injection Grid (AIG) tuning is completed by evaluating the flue gas distribution at the inlet and outlet of the SCR to maximize performance of the SCR and minimum ammonia slip. SCR AIG testing is a vital part to optimizing the effectiveness of the SCR and reducing unwanted ammonia slip. STORM can conduct this testing with our SOAR automated flue gas sampling system if multipoint sampling grids are in place. Testing with this system can dramatically cut down on total costs and manpower requirements.
Reason for Testing:
A facilities SCR is a vital part of their overall emissions control program. Efficient operation of these requires annual checks of the flue gas profile entering and exiting the SCR. Often times imbalances in the “burner belt” of the boiler associated with fuel and air maldistribution will lead to imbalance NOX distribution entering the SCR. If the injection grid is tuned so that ammonia flow is equal to all areas, then you will have certain areas that are over saturated with ammonia and ammonia slip will occur. Other areas that may have higher NOX concentrations will not have the NOX reduction rate that the SCR is designed to achieve. Ammonia slip is a big concern not only for cost concerns but also for ABS formation that can occur downstream in the APH which can severely impact boiler operation. With that in mind, Storm can also measure and quantify ammonia slip rates. So, tuning your AIG grid is something that should be conducted on an annual basis as part of a post outage combustion tune-up program.
Boiler tuning in the past required a team of multiple field technicians manually traversing the boiler and associated flue gas duct work only to be able to complete a few tests per day. Furthermore, with MATS testing regulations today required boiler tune ups to be completed, many facilities that operate with a spare pulverizer need to complete this tune up under each mill configuration and manual traverses of the duct could drive up the costs of this testing. With all that in mind, Storm developed, in house, it’s SOAR system that will connect to a plant existing installed multipoint sampling grid will automatically cycle through up to 96 test points, measure and record an average flue gas measurement for each point. Storm’s system will also automatically record flue gas temperatures if Type “K” thermocouples are installed as well
Reason for Testing:
Storm’s SOAR system significantly cuts down on the manpower and manhours required to conduct in depth boiler tuning utilizing a backend grid at the economizer outlet. Often only a single Storm representative is needed to conduct the boiler tuning if plant staff can assist with burner adjustments, etc. The system can be programmed in the field to adjust sample times to collect a larger or smaller sample size for averaging. At the end of the test, the data can be compiled into many formats to graphically present the flue gas distribution throughout the duct to allow Storm and/or plant engineers to make informed decisions when tuning the boiler for optimum combustion.
Testing Equipment:
ASME PTC Testing
Storm’s staff is equipped with the experience and expertise to conduct testing in accordance with ASME PTC test codes at your facility. Storm often conducts abbreviated versions of these tests during routine testing to provide our customers with a quick and more cost effective evaluation of their boiler’s efficiency, fan performance or air heater performance but it some cases this will not do and a full blown ASME test is required.
Reason for Testing:
Complete ASME PTC tests are often required following the new construction of a boiler or installation of a new piece of equipment that carries guarantees. Storm’s team has the equipment and knowledge to complete this testing and calculations associated with several ASME performance test codes. This testing provides the most accurate, with minimum uncertainty, method for testing the boiler efficiency, air heater performance, fan performance or overall plant performance.
ASME Tests that STORM can Perform:
- ASME PTC 4.0
- ASME PTC 4.3
- ASME PTC 46
- ASME PTC 11
Air Heater Testing
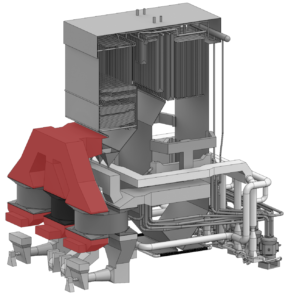
Air Heater testing can be utilized to quantify flue gas constituents and properties such as CO, NOX, O2, temperature, and static pressure. Data derived from this testing can provide powerful knowledge for a facility about the combustion taking place in the boiler as well as air heater performance. An abbreviated air heater performance test can be completed typically in less than one hour and utilizing the calculations provided with the ASME PTC 4.3 test code an accurate assessment of the performance of your air heater can be provided.
Reason for Testing:
- Boiler Tuning (In conjunction with furnace exit testing/boiler outlet testing)
- Addressing imbalances in Oxygen (O2), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Nitrogen oxides (NOX)
- Quantifying air heater performance
- X-Ratio
- Gas Side Efficiency
- Corrected Gas Outlet Temperature
- Gas Side Air Heater Leakage (Oxygen Rise)
- Gas Side Pressure Drop
- Boiler efficiency
- In conjunction with flyash sampling an abbreviated boiler efficiency can be determined based off PTC 4.0
Testing Equipment
- Gas Sampling Conditioner Kit
- Boiler Exit Probe
- Flyash Sampling Probe
- Portable Gas Analyzer
Secondary Air Testing & Calibration

Testing to measure the temperature and the mass airflow going to the burners. 75% to 90% of total airflow is Secondary Airflow (plus Overfire Airflow) and should be closely measured and controlled for optimizing unit performance. Older boilers can succumb to air in leakage that will negatively impact combustion within the furnace. However, if the secondary air flow is accurately measured and controlled the air in leakage can be identified before it becomes too late. Furthermore, Overfire Airflow that takes off of the Secondary Air system must be controlled accurately to optimize combustion and ensure good reliability of the boiler when operating with a Low NOX firing system.
Reason for Testing:
To measure and/or calibrate a newly installed secondary airflow element or existing airflow element to within Storm’s recommended ±3% deviation and to verify accurate temperature indication.
Testing Equipment:
- Forward / Reverse Pitot Tube
- Fecheimer Probe (Optional)
- Five Hole (3D) Probe (Optional)
- Manometers
Primary Air Testing & Calibration
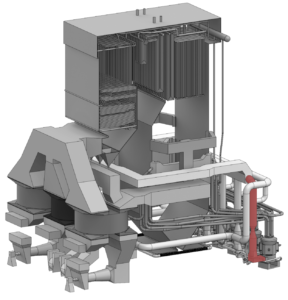
Testing to measure the temperature and the mass airflow going to the Pulverizers. 10% to 20% of total airflow is Primary Airflow and should be closely measured and controlled for optimizing pulverizer and unit performance. Primary airflow is only a small portion of the total air supplied to your boiler BUT it is extremely important that it is measured and controlled accurately.
Reason for Testing:
To measure and/or calibrate a newly installed primary airflow element or existing airflow element to within Storm’s recommended ±3% deviation and to verify accurate temperature indication.
Testing Equipment:
- Forward / Reverse Pitot Tube
- Fecheimer Probe (Optional)
- Five Hole (3D) Probe (Optional)
- Manometers
Clean Air Balancing - Fuel Lines
Balancing system resistance of fuel lines on clean air is the first phase of a comprehensive fuel and air balancing program. It is important to remember that clean air balancing is an important factor and the first step in optimizing pulverizer fuel and air distribution to the burners.
Reason for Testing:
- Establish a similar system resistance for each coal line on a balanced air flow basis.
- Provide a correlation between fuel line “dirty air” and clean air velocities.
- Clean air balancing is an integral part of fuel line air to fuel ratio balancing which incorporates air, as well as fuel balancing.
- To ensure the minimum fuel line velocity is maintained after optimization of primary air flow by eliminating the pipes with low airflow.
Fuel fineness and distribution are prerequisites to achieving the best furnace effectiveness for low-NOx burner performance, slagging, and steam cycle performance. When fuel and air are flowing through the pipes to each burner equally and the quality of the fuel is within specific guidelines, then the pulverized fuel system is balanced and optimized.
Testing Equipment:
- Pitot Tube
- Digital Manometer
- Static / Temperature Probe
- Digital Thermometer
Pulverizer Performance Testing- Fuel Lines

Balanced air and fuel flow, as well as good coal fineness, are essential for optimizing combustion. Optimum fuel balance is achieved through a combined effort aimed at balancing clean air flows, correct air/fuel ratio control, improving pulverizer grinding efficiency (improved fineness) and classifier timing and condition. This testing allows STORM to evaluate how well the pulverizer is performing
Reason for Testing:
Dirty airflow testing and isokinetic coal sampling are performed to:
- Ascertain the dirty airflow and fuel flow balances for each mill.
- Determine the mill grinding performance through coal fineness analysis.
- Provide a correlation between fuel line “dirty air” velocities and fuel balance.
- Determine the air to fuel ratio needed for optimum pulverizer performance.
- To ensure the minimum fuel line velocity is maintained after optimization of primary air flow to improve flame stability at lower loads and reduce fuel line stoppages.
Together, the data provides a window into coal pipe performance that is an important precursor to optimizing furnace combustion efficiency. Fuel fineness and distribution are prerequisites to achieving the best furnace effectiveness for low-NOx burner performance, slagging, and steam cycle performance. When fuel and air are flowing through the pipes to each burner equally and the quality of the fuel is within specific guidelines, then the system is balanced. These measurements play a crucial role in any diagnostic combustion testing plan.
Testing Equipment:
Pulverizer Performance Testing- Fuel Lines

Balanced air and fuel flow, as well as good coal fineness, are essential for optimizing combustion. Optimum fuel balance is achieved through a combined effort aimed at balancing clean air flows, correct air/fuel ratio control, improving pulverizer grinding efficiency (improved fineness) and classifier timing and condition. This testing allows STORM to evaluate how well the pulverizer is performing
Reason for Testing:
Dirty airflow testing and isokinetic coal sampling are performed to:
- Ascertain the dirty airflow and fuel flow balances for each mill.
- Determine the mill grinding performance through coal fineness analysis.
- Provide a correlation between fuel line “dirty air” velocities and fuel balance.
- Determine the air to fuel ratio needed for optimum pulverizer performance.
- To ensure the minimum fuel line velocity is maintained after optimization of primary air flow to improve flame stability at lower loads and reduce fuel line stoppages.
Together, the data provides a window into coal pipe performance that is an important precursor to optimizing furnace combustion efficiency. Fuel fineness and distribution are prerequisites to achieving the best furnace effectiveness for low-NOx burner performance, slagging, and steam cycle performance. When fuel and air are flowing through the pipes to each burner equally and the quality of the fuel is within specific guidelines, then the system is balanced. These measurements play a crucial role in any diagnostic combustion testing plan.
Testing Equipment:
- Isokinetic Coal Sampling Kit
Clean Air Balancing - Fuel Lines

Balancing system resistance of fuel lines on clean air is the first phase of a comprehensive fuel and air balancing program. It is important to remember that clean air balancing is an important factor and the first step in optimizing pulverizer fuel and air distribution to the burners.
Reason for Testing:
- Establish a similar system resistance for each coal line on a balanced air flow basis.
- Provide a correlation between fuel line “dirty air” and clean air velocities.
- Clean air balancing is an integral part of fuel line air to fuel ratio balancing which incorporates air, as well as fuel balancing.
- To ensure the minimum fuel line velocity is maintained after optimization of primary air flow by eliminating the pipes with low airflow.
Fuel fineness and distribution are prerequisites to achieving the best furnace effectiveness for low-NOx burner performance, slagging, and steam cycle performance. When fuel and air are flowing through the pipes to each burner equally and the quality of the fuel is within specific guidelines, then the pulverized fuel system is balanced and optimized.
Testing Equipment:
- Pitot Tube
- Digital Manometer
- Static / Temperature Probe
- Digital Thermometer
Primary Air Testing & Calibration

Testing to measure the temperature and the mass airflow going to the Pulverizers. 10% to 20% of total airflow is Primary Airflow and should be closely measured and controlled for optimizing pulverizer and unit performance. Primary airflow is only a small portion of the total air supplied to your boiler BUT it is extremely important that it is measured and controlled accurately.
Reason for Testing:
To measure and/or calibrate a newly installed primary airflow element or existing airflow element to within Storm’s recommended ±3% deviation and to verify accurate temperature indication.
Testing Equipment:
- Forward / Reverse Pitot Tube
- Fecheimer Probe (Optional)
- Five Hole (3D) Probe (Optional)
- Manometers
Secondary Air Testing & Calibration

Testing to measure the temperature and the mass airflow going to the burners. 75% to 90% of total airflow is Secondary Airflow (plus Overfire Airflow) and should be closely measured and controlled for optimizing unit performance. Older boilers can succumb to air in leakage that will negatively impact combustion within the furnace. However, if the secondary air flow is accurately measured and controlled the air in leakage can be identified before it becomes too late. Furthermore, Overfire Airflow that takes off of the Secondary Air system must be controlled accurately to optimize combustion and ensure good reliability of the boiler when operating with a Low NOX firing system.
Reason for Testing:
To measure and/or calibrate a newly installed secondary airflow element or existing airflow element to within Storm’s recommended ±3% deviation and to verify accurate temperature indication.
Testing Equipment:
- Forward / Reverse Pitot Tube
- Fecheimer Probe (Optional)
- Five Hole (3D) Probe (Optional)
- Manometers
Furnace Exit Testing

Testing to measure the temperature and gas constituents of at the furnace exit. Furnace exit testing is a vital part of improving overall combustion and optimizing unit performance.
Reason for Testing:
Furnace Exit Testing is important because it quantifies the concentration of Oxygen (O2 , %), Nitrous Oxides (NOX ppm) and Carbon Monoxide (CO , ppm) inside the furnace, typically at the nose arch elevation. One of the most important reasons for conducting this test is determining the actual excess oxygen levels within the furnace. Balanced draft boilers over time will develop leaks that will allow tramp air to infiltrate the boiler and flue gas duct work. If the tramp air is introduced into the system upstream of the excess oxygen probes then the boiler airflow control will account for this additional oxygen and reduce the total air to the boiler for combustion, often times leaving the furnace in a severely sub-stoichiometric firing condition with reducing atmospheres present. Furthermore, Furnace Exit Testing allows the plant to quantify the Furnace Exit Gas Temp (FEGT) as well as make a profile that depicts the specific environment of the furnace based on temperatures and gas constituents. This is important because it reveals all area’s of concerns inside the furnace. Common concerns found inside the boiler are reducing atmospheres, high FEGT, and low oxygen. These issues directly relate to an increase in slagging and decreased performance/efficiency.
Testing Equipment:
- High Velocity Thermocouple (HVT) Probe
- Gas Sampling Conditioner Kit
- Portable Gas Analyzer
Boiler Performance Testing

Storm evaluates boiler performance by measuring flue gas constituents of temperature, oxygen, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides throughout the boiler and back-pass. Measurements typically obtained by Storm include the following locations:
- Furnace Exit (At the nose arch or just above the nose arch)
- Economizer Exit/Air Heater Inlet
- Air Heater Outlet
Reason for Testing:
Measurements at these locations can uncover areas of concern such as, reducing atmospheres, high FEGT, slagging and decreased performance, in-leakage, etc. Storm still utilizes a water-cooled HVT probe when conducting a complete boiler performance test. This is a very important step, that other companies often overlook. By evaluating the in-furnace conditions of the boiler our teams can get a better idea of the root cause of combustion related issues. Obtaining and analyzing flyash LOI is also critical in determining overall performance. By utilizing these locations, an abbreviated boiler efficiency can be obtained along with APH performance and system leakage of the boiler and APH.
Testing Equipment:
- High Velocity Thermocouple (HVT) Probe
- Gas Sampling Conditioner Kit
- Boiler Exit Probe
- Flyash Sampling Probe
- Storm’s SOAR System (Automated Flue Gas Sampling)
- Portable Gas Analyzer
Air Heater Testing

Air Heater testing can be utilized to quantify flue gas constituents and properties such as CO, NOX, O2, temperature, and static pressure. Data derived from this testing can provide powerful knowledge for a facility about the combustion taking place in the boiler as well as air heater performance. An abbreviated air heater performance test can be completed typically in less than one hour and utilizing the calculations provided with the ASME PTC 4.3 test code an accurate assessment of the performance of your air heater can be provided.
Reason for Testing:
- Boiler Tuning (In conjunction with furnace exit testing/boiler outlet testing)
- Addressing imbalances in Oxygen (O2), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Nitrogen oxides (NOX)
- Quantifying air heater performance
- X-Ratio
- Gas Side Efficiency
- Corrected Gas Outlet Temperature
- Gas Side Air Heater Leakage (Oxygen Rise)
- Gas Side Pressure Drop
- Boiler efficiency
- In conjunction with flyash sampling an abbreviated boiler efficiency can be determined based off PTC 4.0
Testing Equipment
- Gas Sampling Conditioner Kit
- Boiler Exit Probe
- Flyash Sampling Probe
- Portable Gas Analyzer
Boiler tuning in the past required a team of multiple field technicians manually traversing the boiler and associated flue gas duct work only to be able to complete a few tests per day. Furthermore, with MATS testing regulations today required boiler tune ups to be completed, many facilities that operate with a spare pulverizer need to complete this tune up under each mill configuration and manual traverses of the duct could drive up the costs of this testing. With all that in mind, Storm developed, in house, it’s SOAR system that will connect to a plant existing installed multipoint sampling grid will automatically cycle through up to 96 test points, measure and record an average flue gas measurement for each point. Storm’s system will also automatically record flue gas temperatures if Type “K” thermocouples are installed as well
Reason for Testing:
Storm’s SOAR system significantly cuts down on the manpower and manhours required to conduct in depth boiler tuning utilizing a backend grid at the economizer outlet. Often only a single Storm representative is needed to conduct the boiler tuning if plant staff can assist with burner adjustments, etc. The system can be programmed in the field to adjust sample times to collect a larger or smaller sample size for averaging. At the end of the test, the data can be compiled into many formats to graphically present the flue gas distribution throughout the duct to allow Storm and/or plant engineers to make informed decisions when tuning the boiler for optimum combustion.
Testing Equipment:
- Mulitpoint gas sampling probes
- SOAR System
AIG (SCR) Tuning

Ammonia Injection Grid (AIG) tuning is completed by evaluating the flue gas distribution at the inlet and outlet of the SCR to maximize performance of the SCR and minimum ammonia slip. SCR AIG testing is a vital part to optimizing the effectiveness of the SCR and reducing unwanted ammonia slip. STORM can conduct this testing with our SOAR automated flue gas sampling system if multipoint sampling grids are in place. Testing with this system can dramatically cut down on total costs and manpower requirements.
Reason for Testing:
A facilities SCR is a vital part of their overall emissions control program. Efficient operation of these requires annual checks of the flue gas profile entering and exiting the SCR. Often times imbalances in the “burner belt” of the boiler associated with fuel and air maldistribution will lead to imbalance NOX distribution entering the SCR. If the injection grid is tuned so that ammonia flow is equal to all areas, then you will have certain areas that are over saturated with ammonia and ammonia slip will occur. Other areas that may have higher NOX concentrations will not have the NOX reduction rate that the SCR is designed to achieve. Ammonia slip is a big concern not only for cost concerns but also for ABS formation that can occur downstream in the APH which can severely impact boiler operation. With that in mind, Storm can also measure and quantify ammonia slip rates. So, tuning your AIG grid is something that should be conducted on an annual basis as part of a post outage combustion tune-up program.
Testing Equipment:
- Storm’s SOAR System (Automated Flue Gas Sampling System)
- Multipoint Flue Gas Sampling Probes
STORM testing services also includes the ability and knowledge to complete environmental emissions testing for particulate matter (EPA Methods 5 and 17), NOX, CO and SO2.
Reason for Testing:
To better understand the efficiency of your air pollution control equipment. Particulate matter testing can be utilized to evaluate the flyash loading in your system or to determine the effectiveness of your ESP or baghouse. Further, flue gas testing can be done to evaluate the flue gas profiles and concentrations from the furnace exit to the ID fan in order to provide our customer with the flue gas measurements needed
Testing Equipment:
- Flue Gas Sampling Probes (i.e .HVT, boiler exit, multipoint, etc.)
- Gas Conditioning Equipment
- Gas Anlyzers
- Flyash Sampling Probes
ASME PTC Testing
Storm’s staff is equipped with the experience and expertise to conduct testing in accordance with ASME PTC test codes at your facility. Storm often conducts abbreviated versions of these tests during routine testing to provide our customers with a quick and more cost effective evaluation of their boiler’s efficiency, fan performance or air heater performance but it some cases this will not do and a full blown ASME test is required.
Reason for Testing:
Complete ASME PTC tests are often required following the new construction of a boiler or installation of a new piece of equipment that carries guarantees. Storm’s team has the equipment and knowledge to complete this testing and calculations associated with several ASME performance test codes. This testing provides the most accurate, with minimum uncertainty, method for testing the boiler efficiency, air heater performance, fan performance or overall plant performance.
ASME Tests that STORM can Perform:
- ASME PTC 4.0
- ASME PTC 4.3
- ASME PTC 46
- ASME PTC 11
In addition to testing services, Storm’s professional team has the experience and expertise to support your next scheduled or forced outage with performance inspections of the burners, pulverizers, fans, flue gas ductwork, penthouse and air heater. Storm can also provide in-depth management of air heater outage overhauls from planning to execution of the overhaul.
Reason for Inspections:
- Throughout the years Storm has found that coupling the professional testing services along with outage support through performance inspections that performance challenges associated with poor combustion, elevated heat rates and decreased reliability can be effectively improved. Storm’s personnel often complete inspections on overlooked items that are critical to combustion but are too tedious to be included in many outage plans, such as burner centering, stroking burner registers and damper inspections to name a few. Furthermore, Storm’s fabrication shop can provide last minute fabricated components that may be needed once identified during your outage.
- Storm also has the expertise to provide complete outage services for your upcoming overhaul on regenerative Ljungstrom air heaters. Storm can provide the outage planning, scheduling and provide you with quotes for replacement parts to ensure your air heater is performing well following the outage.








